Importing data
grit offers a consistent data upload experience across most parts of the system. The import process follows a standardised sequence of steps, typically requiring the same user inputs regardless of context. Uploaded data is expected to be in a delimiter-separated format (such as CSV or TSV) with headers or in supported specialised formats, where applicable. In some cases, additional information may be required, but these requirements are clearly indicated and often pre-filled to ensure a smooth and transparent experience.
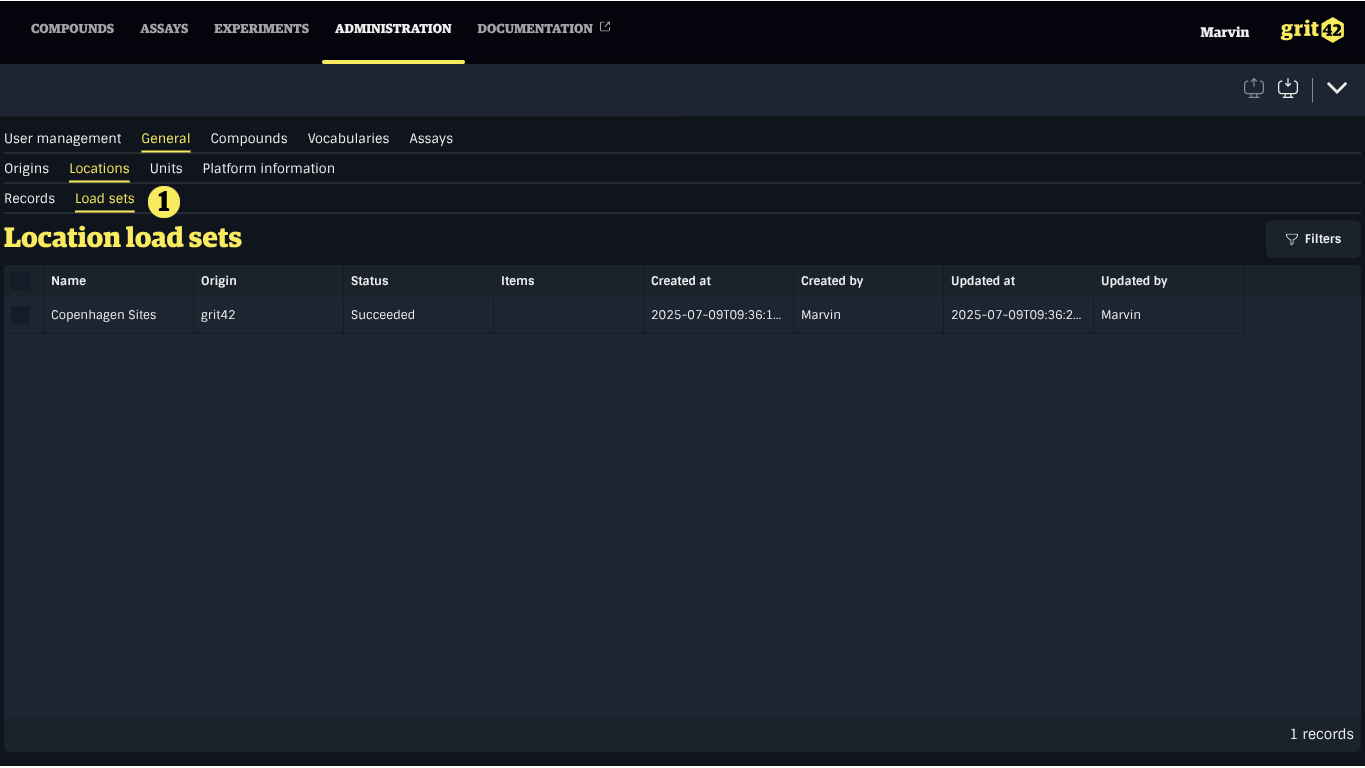
Imported data sets are referred to as Load Sets. A Load Set can be undone to remove all associated data from the system, provided the data is not linked to other entities.
When a view supports data import, the Import toolbar action will be enabled. The import flow is started by clicking the Import toolbar action. Some views may support importing different kind of data, requiring choosing the appropriate data type in a menu before continuing.
Uploading a Data Set
The first step in the import process prompts to provide a text-based data set along with metadata describing the content to be imported.
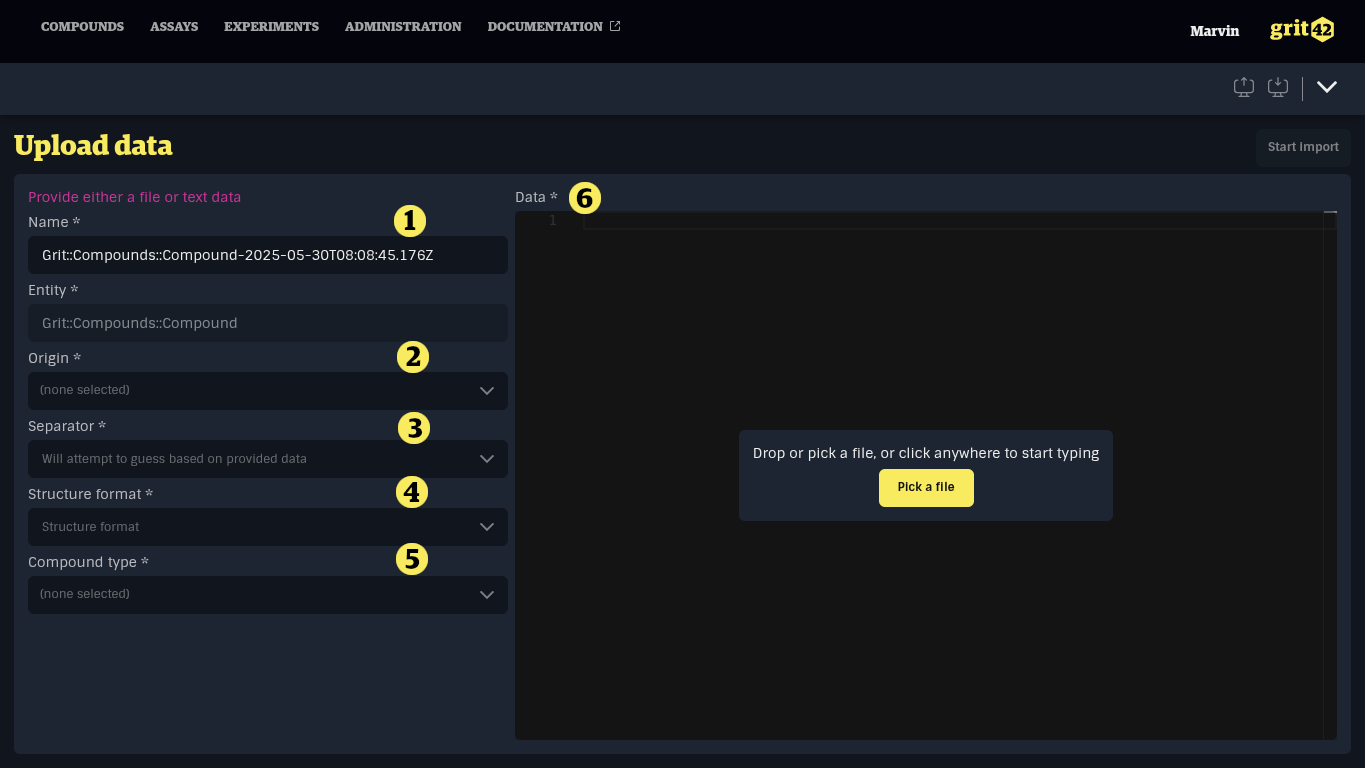
- The name of the Load Set. This is pre-filled based on the data type and the current date, but it is recommended to provide a more meaningful name for future reference.
- The Origin of the data. This helps track where the source of the data set.
- The separator used in the data set. When a file is added, the system attempts to detect the delimiter based on the file's contents.
- A field specific to the kind of data being uploaded. Here, the format of the molecular structures in the file.
- A field specific to the kind of data being uploaded. Here, the compound type.
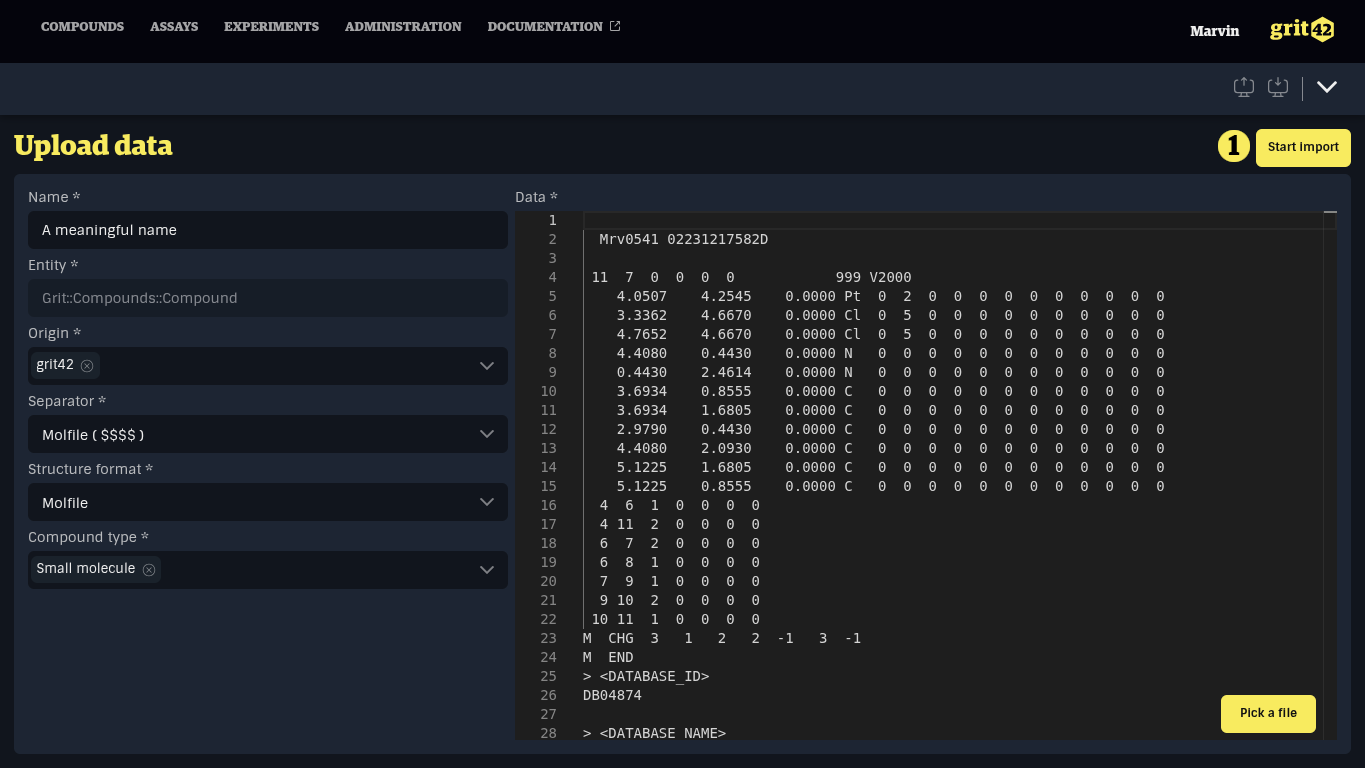
- The data set itself. A data set can be added by:
- dropping a file in the dark upload area
- opening the file explorer and selecting a file
- clicking the dark area and manually typing or pasting a selection from a spreadsheet or another text editor
In most spreadsheet applications, selecting an area of the spreadsheet and copying it will result in delimiter-separated text which can be pasted directly into the input area.
When all fields have been filled and a data set has been added, click on the Start import above the data set to continue.
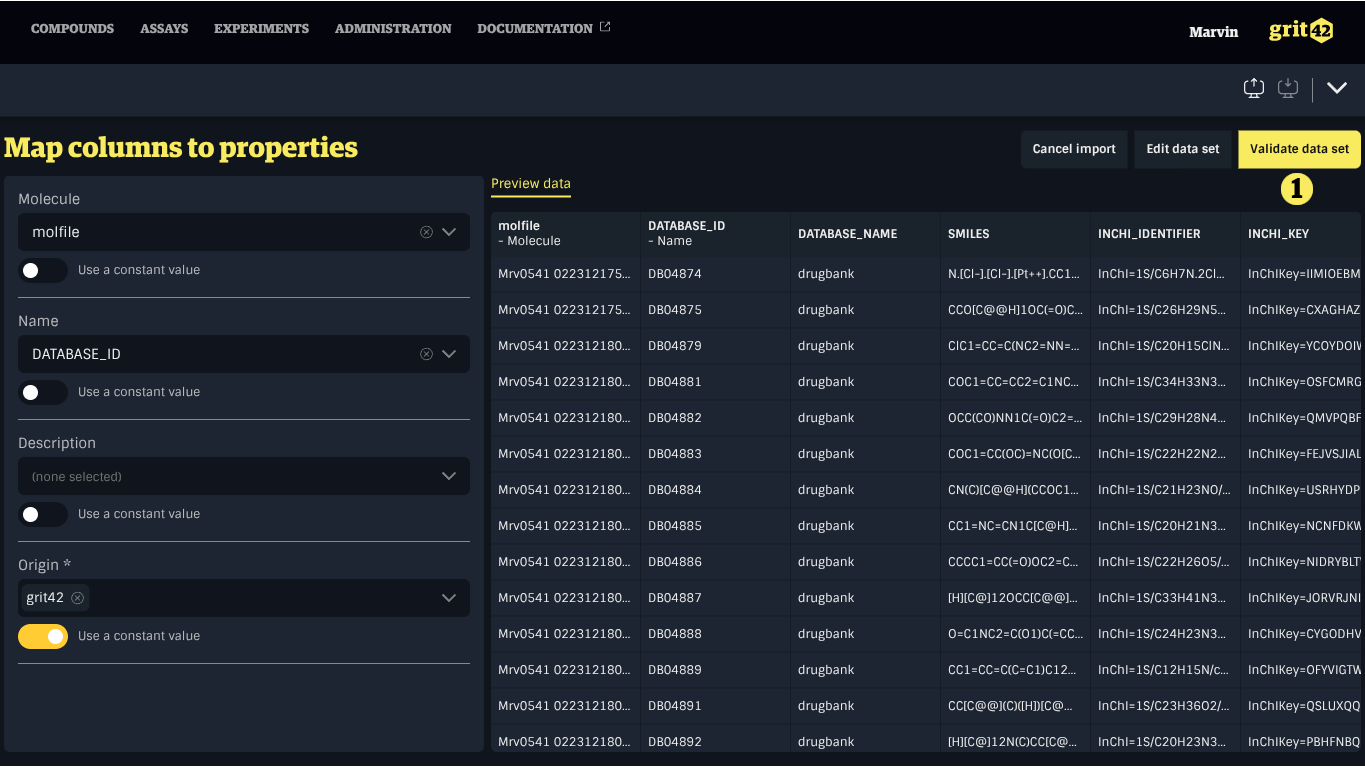
Mapping the Data Set
The second step in the import process consists of mapping columns from the data set to properties in the system.
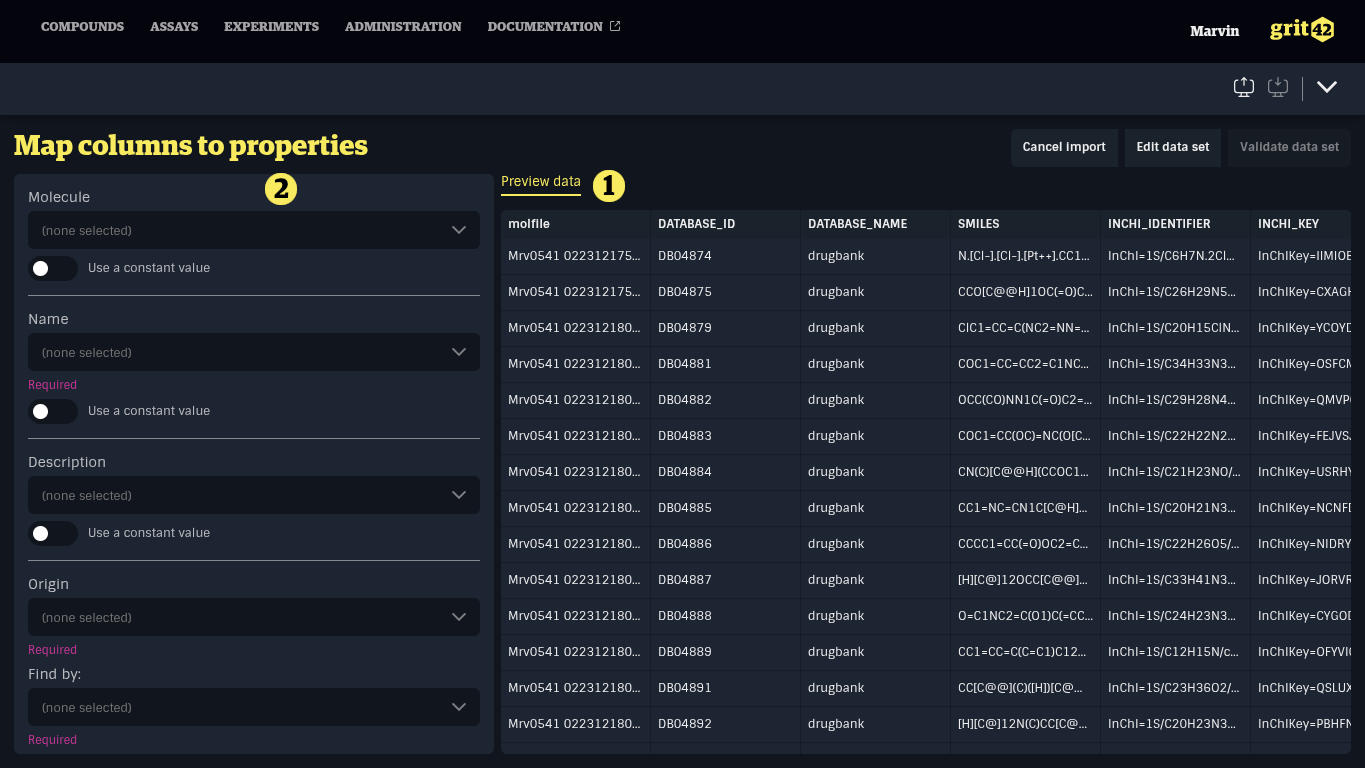
- A preview of the data set
- The form to map data set column to properties in grit
There are two categories of properties: simple properties and entity properties.
Simple properties, such as numbers, text, dates, and booleans, only need to be mapped to a column in the data set.
Entity properties refer to more complex data types, such as Units or Origins. Like simple properties, they must be mapped to a column in the data set, but they also require a unique field to identify the corresponding record in the database using the value from the data set.
There may be cases where a property does not have a corresponding column in the data set. If the missing property has the same value for all records, you can specify a default value to be applied uniformly. However, if the value varies between records, the data set should be updated accordingly, or the import should be cancelled and restarted with a complete data set.
Data set columns with headers matching property names will be mapped automatically.
Mapping a simple property
To map a simple property to a column, select the appropriate column from the dropdown menu under the property name in the form on the left.
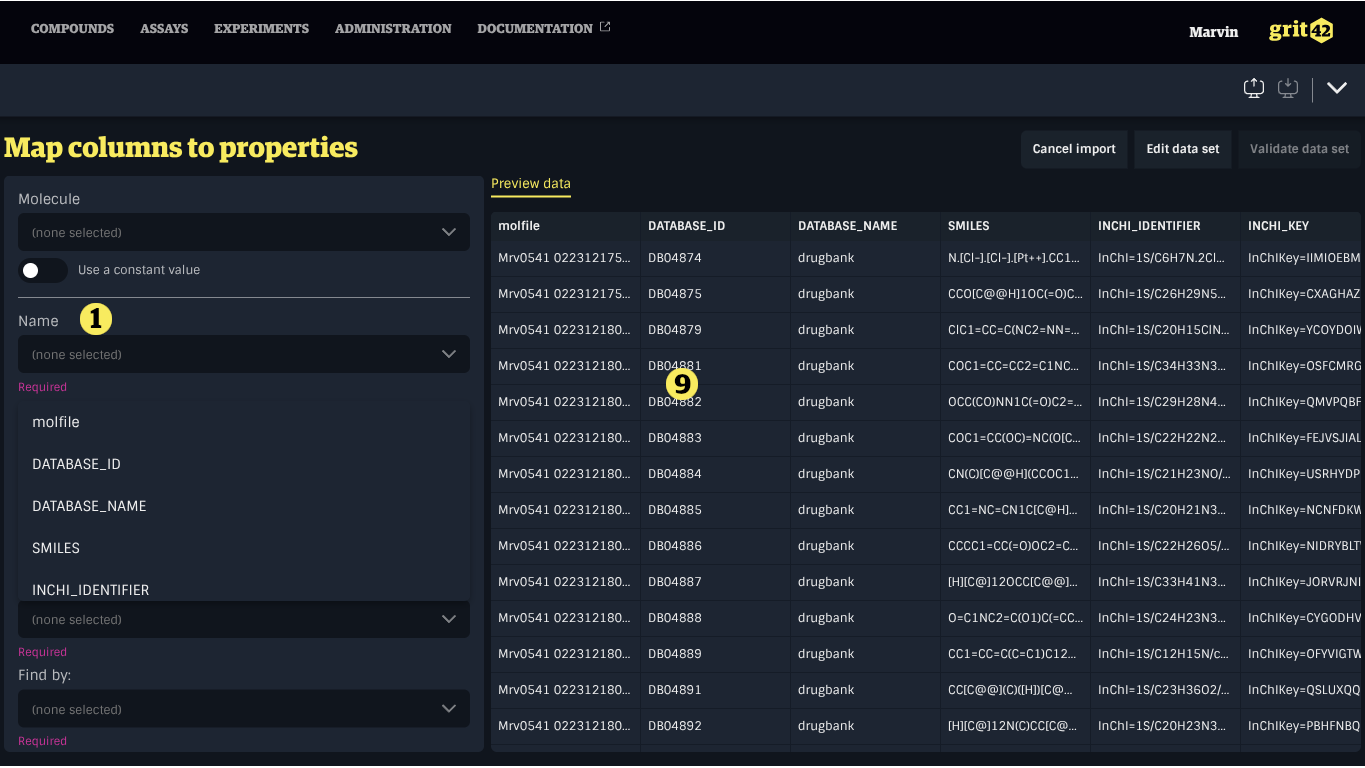
Mapping an entity property
To map an entity property to a column, first select the appropriate column from the dropdown menu under the property name in the form on the left. Then, use the dropdown menu labelled Find by to choose the entity property that should be used to match the record based on the value in the data set.
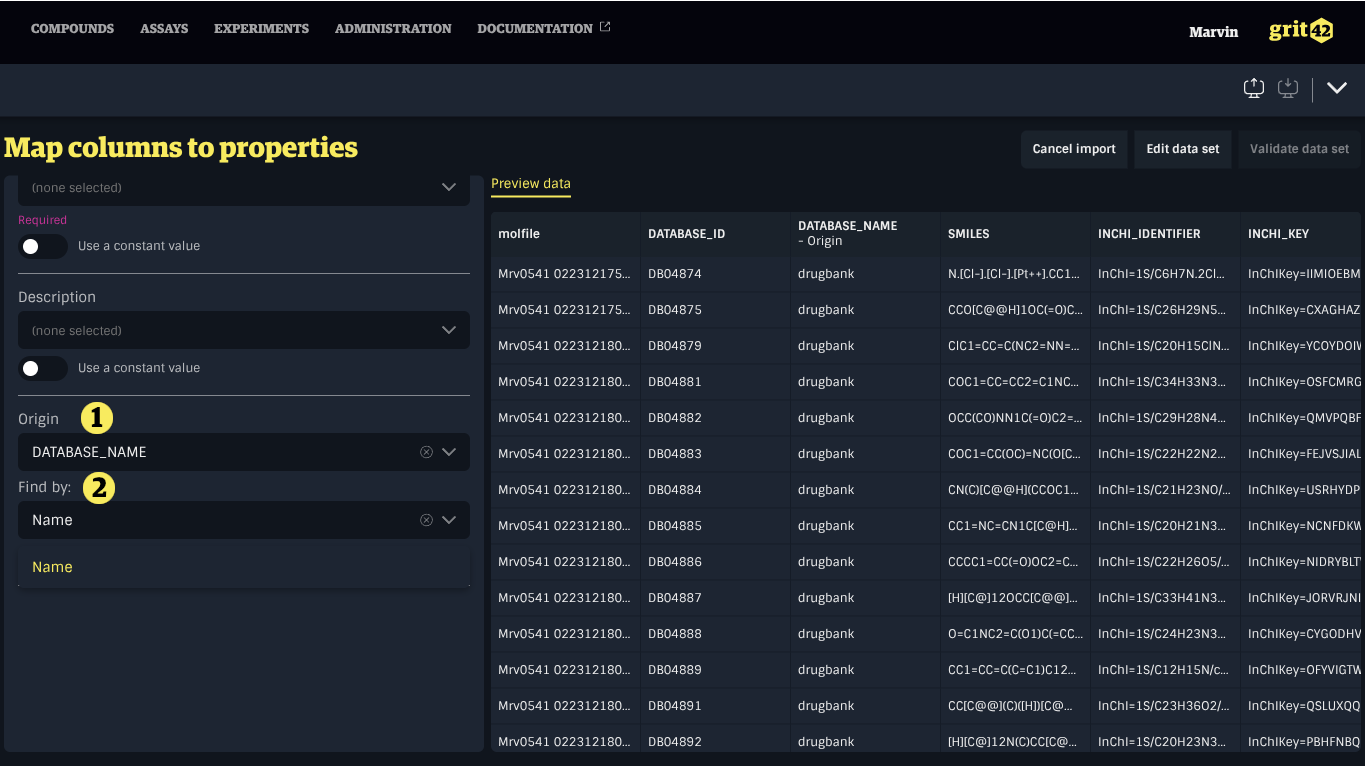
Only unique properties show up in the Find by menu to ensure the correct record is resolved.
Using a constant value
To use a constant value, enable the switch labelled Use a constant value located below the property’s dropdown menu. This will replace the dropdown with an input field where a default value can be entered.
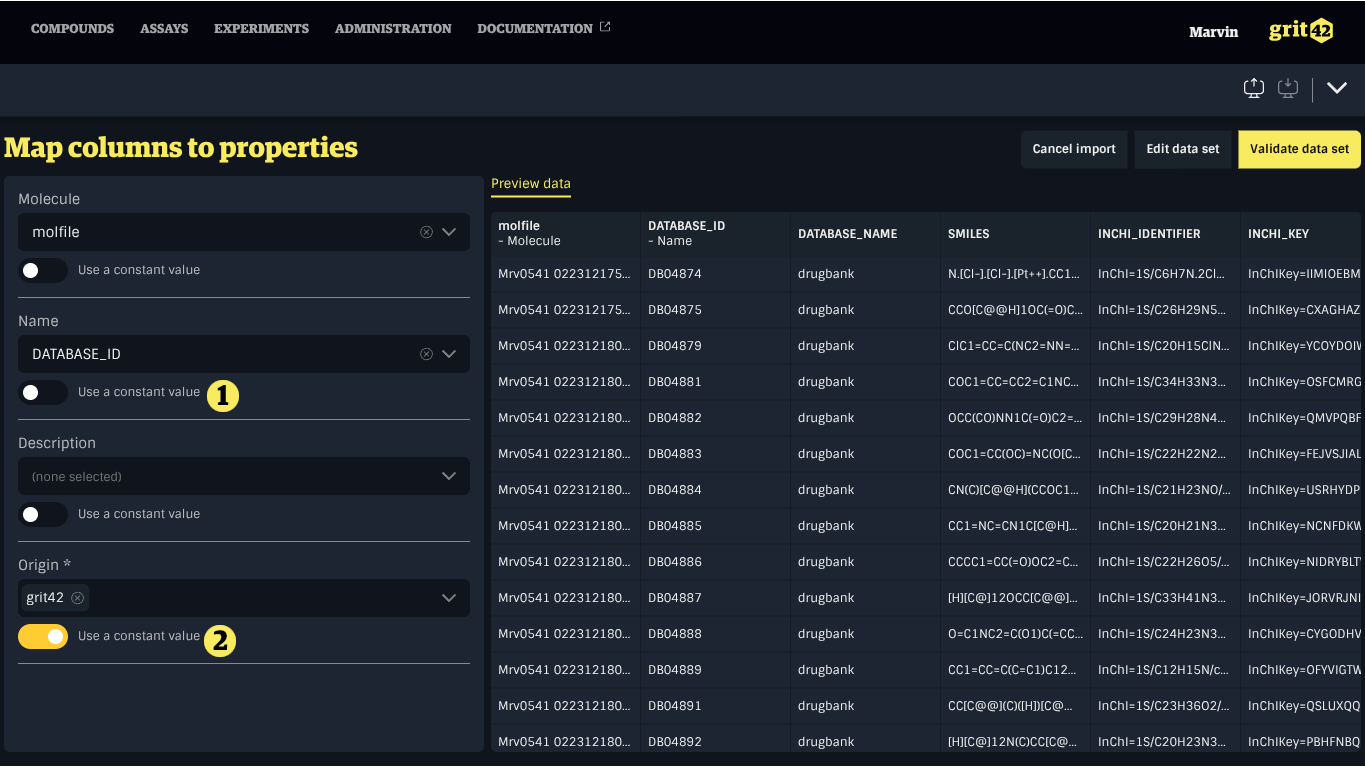
- A property mapped to a data set column
- A property set to a constant value
Validating the Data Set
The third step in the import process is validation. Once all required properties have been configured, the data set can be validated by clicking the Validate data set button.
Depending on system load and the size of the data set, the validation process may take some time.
If the data set contains errors (such as missing or incorrectly formatted values, unresolved entities, or conflicting unique constraints) or warnings, additional tabs will appear next to the Data Set Preview tab, showing:
- Errors: A detailed list of all errors
- Errored rows: All rows that produced errors
- Warnings: A detailed list of all warnings
These lists can be exported as CSV files for further processing by clicking the Export toolbar action in the relevant tab.
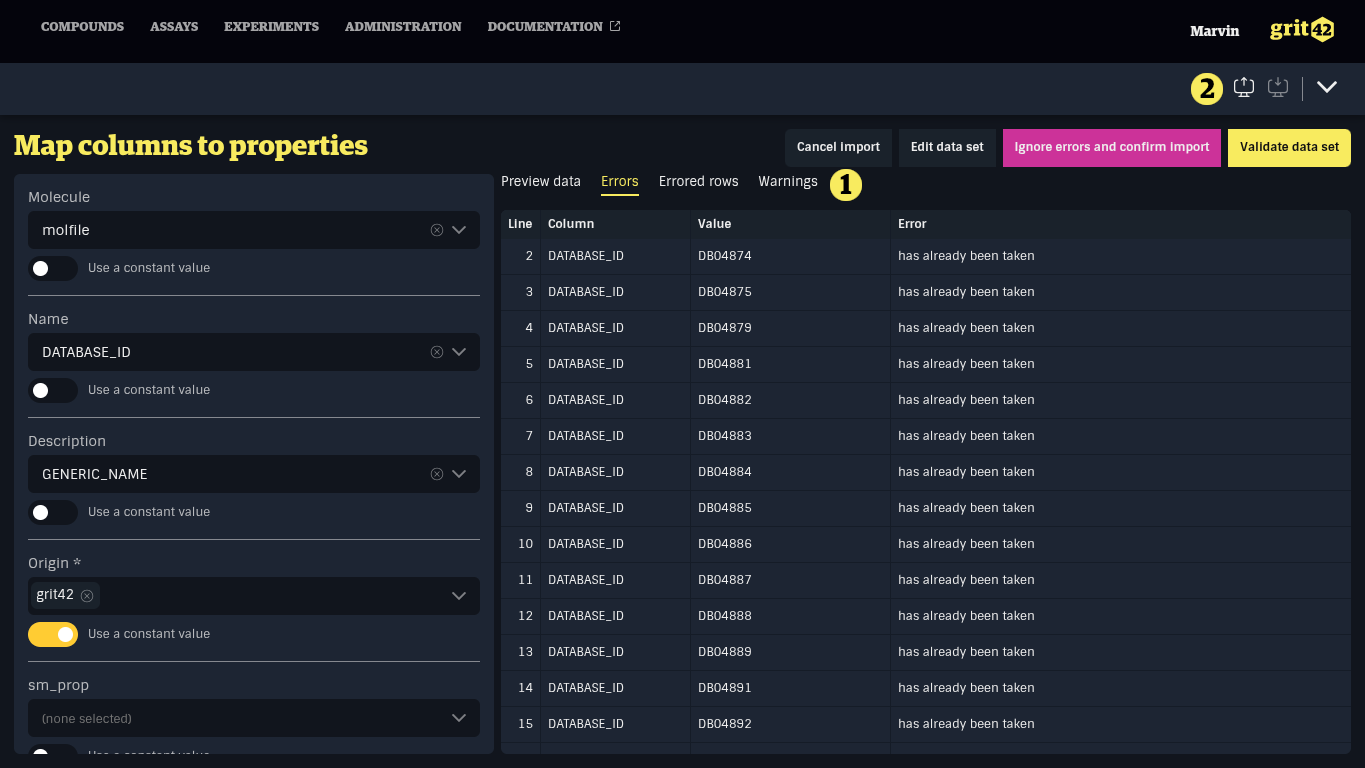
There are three ways to address errors in a data set:
- Edit the data set
- Clicking this button will reveal a text editor where you can manually edit the data or replace the file
- Cancel the import and start over with a clean data set
- Ignore records with errors and proceed with the valid ones
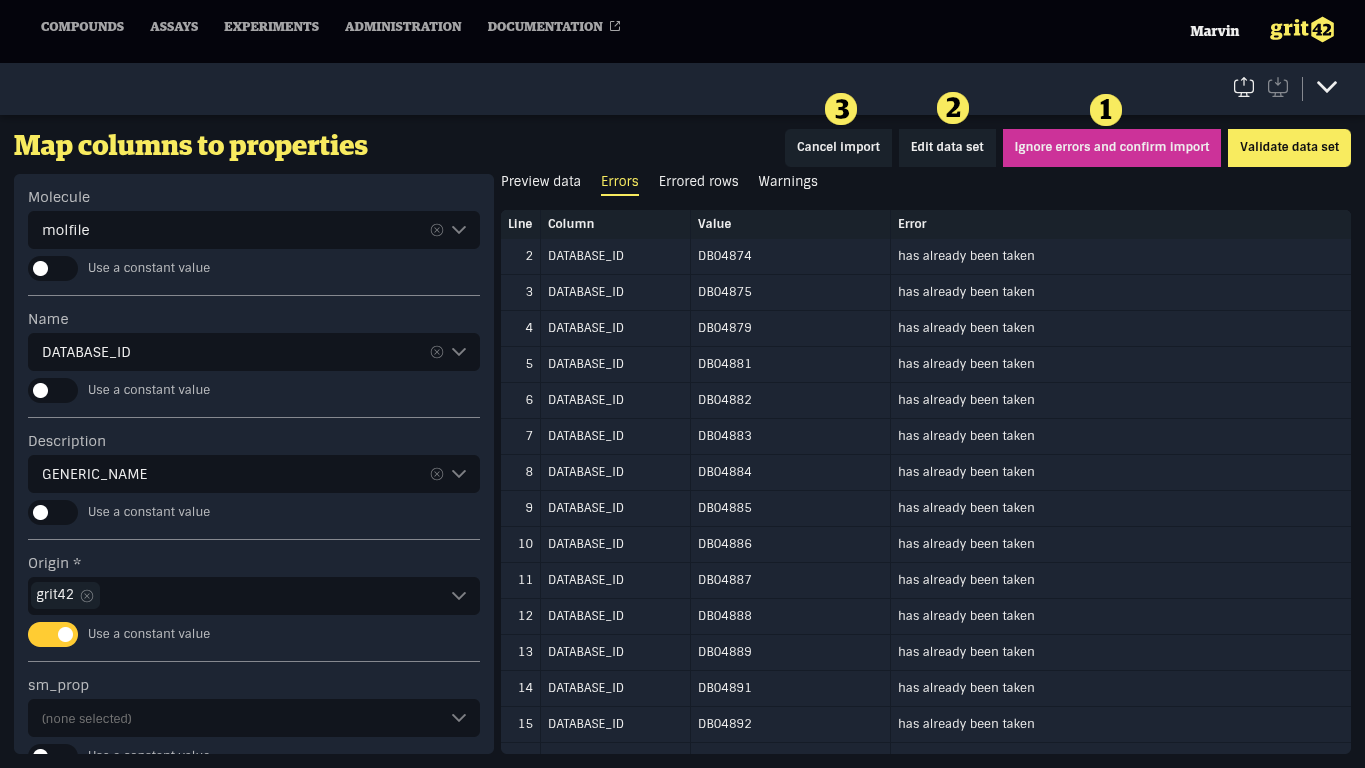
If the data set is free of errors, the property mapping form will be locked, allowing you to review the mappings before confirming.
Reviewing the Loaded Data
The final step in the import process is reviewing the imported records. After confirming a valid Load Set or choosing to proceed with only valid records from an invalid one, the imported data will be displayed in a grid that can be filtered and sorted for inspection.
Specific actions may be available in this view depending on the type of data imported.
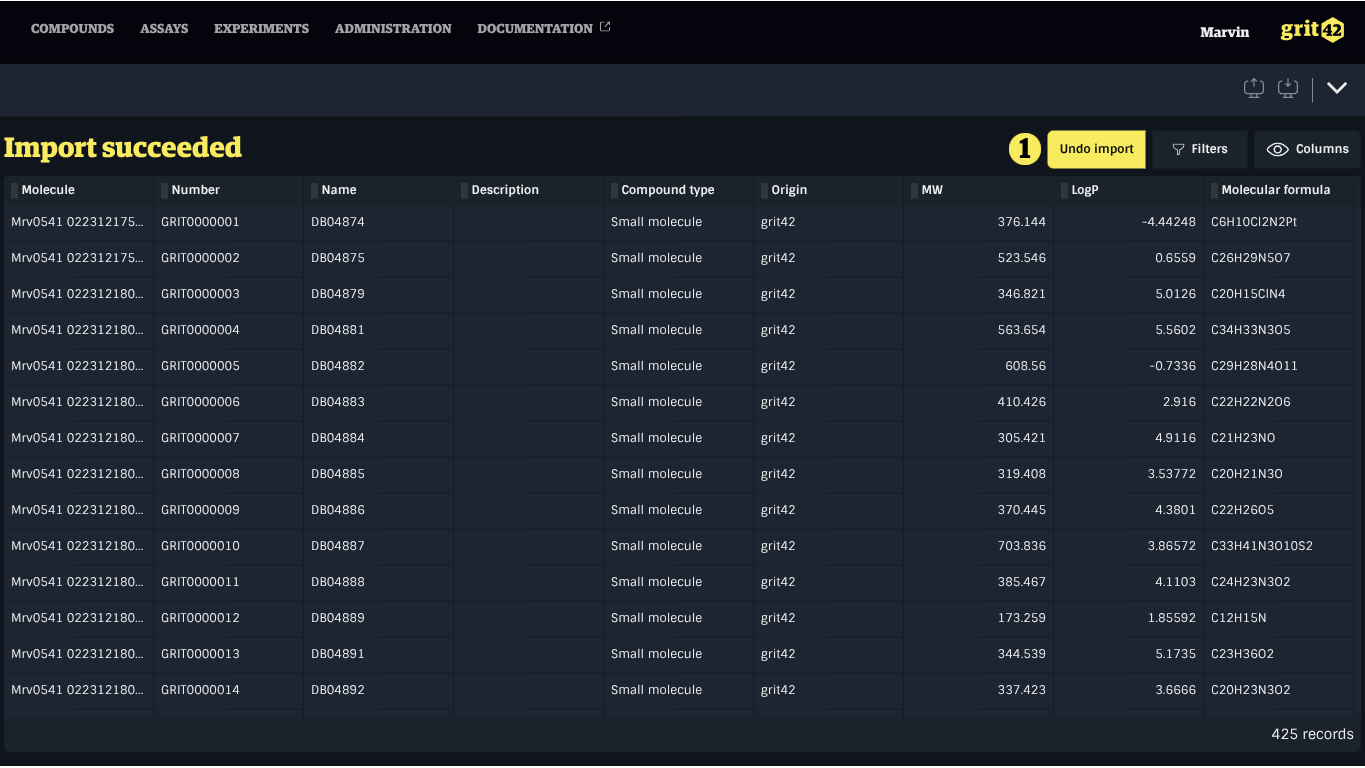
Deleting all records created by a Load Set
All records from a Load Set can be deleted by clicking Undo Import in the final step of the import process, provided none of the records are in use elsewhere in the system. Undoing an import resumes the process at the mapping step, including any previously ignored rows, allowing mappings and data to be modified as needed. The data set will undergo validation again even if no modifications were made.

Finding Load Sets
A list of Load Sets for a given type of data can usually be found close to the view where the import process was started. Click a Load Set in the list to open the importer and continue mapping, edit the data set or undo the import.
The management of Locations in the system is done in the Administration section. All related Load Sets can be found in the tab next to the list of Locations.